Table of contents
Image analysis is a crucial part of computer vision, and it can be divided into several steps, including data acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, and decision making or high-level representation. In this article, we will focus on the third step, feature extraction, which plays a vital role in image analysis.
Features can be classified into three categories: region features, line features, and point features. Each type of feature provides different information about an image and can be used for various computer vision tasks.
Region features
Region features describe the shape or structure of an object or region in an image. These features are calculated based on the properties of the image pixels, such as intensity, color, or texture. They can be used for tasks such as object recognition, segmentation, and classification.
Some common examples of region features include the shape and size of objects, the number and distribution of edges, and the intensity or color distribution of pixels within an object or region.
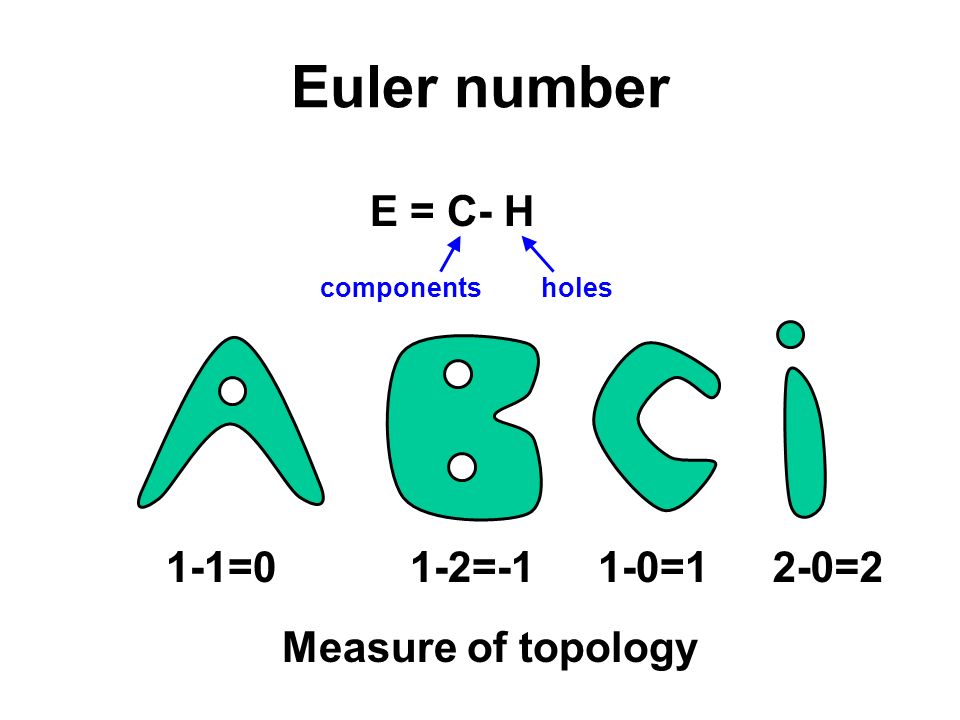
The Euler number can provide additional topological information and improve the accuracy of object recognition and classification algorithms.
Euler number = Number of connected components (C) - Number of holes (H)
E.g.1, Assume the keyboard is a rectangle shape, with no hole:Euler (keyboard) = 1 - 0 = 1
E.g.2, Compute euler number for character 'B':Euler (B) = 1 - 2 = -2
In addition, chain codes can be used to enhance the representation of the shape of an object. It represents the shape by encoding the movement direction of the contour or shape in terms of a compass direction (e.g., north, south, east, west, etc.). The resulting chain code sequence can be used for various computer vision tasks, such as object recognition, shape matching, and image segmentation.

Image source: Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing, vol. 2014, Article ID 896128, 12 pages, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/896128
Texture is a subcategory of region features and refers to the distribution of intensity or color values in an image. The Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) is a statistical approach that represents the relationship between pairs of pixels in an image based on their gray level values and can be used to describe texture.
Line features
Line features describe the lines or edges present in an image. They are important for image recognition and computer vision tasks, as they can be used to identify objects and their boundaries within an image. Line features can be extracted using edge detection algorithms that highlight the sharp changes in intensity or color between adjacent pixels. Once extracted, they can be used for a variety of purposes, such as object recognition, image segmentation, and tracking.
For instance, in a traffic surveillance system, line features can be used to detect the edges of vehicles and track their movement.

Point features
Point features describe unique points on an object, such as corners, tips, or intersections. They can be used to identify individual objects or to track them over time. Point features can be used in computer vision tasks such as object detection, recognition, and tracking. For example, in a traffic surveillance system, point features can be extracted from images of vehicles to identify specific features such as headlights, taillights, or license plates, which can be used to track individual vehicles over time.
In conclusion, feature extraction is a critical step in the image analysis pipeline, and the choice of features to extract will depend on the specific task at hand. Understanding the different types of features, such as region features, line features, and point features, and their uses can help in selecting the most appropriate features for a given task.